Category Archives: Data Governance
Explaining the Path to Data Governance from the Ground Up!
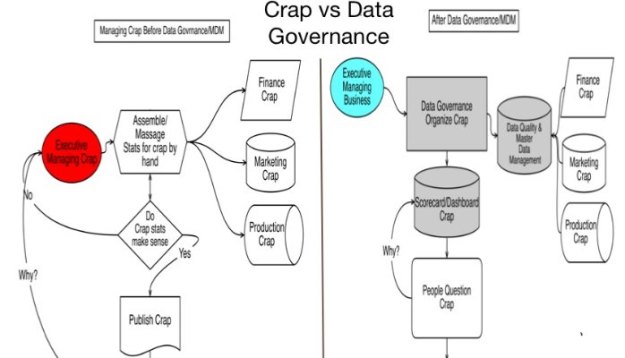
We will explore a methodology for understanding and implementing Data Governance that relies on an ground up approach described by Michael Belcher from Gartner as using ETL and Data Warehouse techniques to build a metadata mart, in order to “boot strap” a Data Governance” effort.
We will discuss the difference between the communication required for data governance and the engineering approach to implementing the “precision” required for MDM, via Data Profiling.
With Data Governance can apply the age old management adage “You get what you inspect, not what you expect” Readers Digest.
We will describe how to implement a data quality dashboard in Excel and how it supports a Data Governance effort in terms of inspection.
Future videos will explore how to build metadata repository as well as the TSQL required to load and update the repository and the data model as well as column and table relationship analysis using the Domain profiling results.
Organic Data Quality vs Machine Data Quality
In reading a few recent blog post on centralized data quality vs. distributed data quality have provoked me to offer another point of view.
Organic distributed data quality provides todays awareness for all current source analysis and problem resolution and they are accomplished manually by individuals in most cases.
In many cases when management or leadership(Folks worried about their jobs) are presented with any type of organized machine based data quality results that can easily be viewed, understood and is permanently available, the usual result is to kill or discredit the messenger.
Automated “Data Quality Scoring” (Profiling + Metadata Mart) brings them from a general “awareness” to a realized state “awarement”.
Awarement is the established form of awareness. Once one has accomplished their sense of awareness they have come to terms with awarement.
It’s one thing to know that alcohol can get you drunk, it quite another to be aware that you are drunk when you are drunk.
Perception = Perception
Awarement = Reality
Departmentral DQ = Awareness
vs
Centralized DQ = Awarement
Share the love… of Data Quality– A distributed approach to Data Quality may result in better data outcomes
Informatica Cloud MDM for Salesforce (formerly Data Scout) Review
Tactically improving Data Quality and incrementally achieving Data Governance and metadata management is a natural path and MDM is the center of that strategy. See Gartner Group’s Applying Data Mart and Data Warehousing Concepts to Metadata Management
In Metadata Mart the Road to Data Governance or Guerilla Data Governance I outline this approach
I’ve just completed a Data Governance Assessment and review of Informatica CLOUD MDM(formerly Data Scout for Salesforce) with my colleague and excellent Solution Architect Baliji Kkarade . The client in this case is interested in implementing Informatica CLOUD MDM in Salesforce , as a tactical approach to improving Data Quality and incrementally improving Data Governance . I’d like to aknowledge the incredible insight I gained from Balaji Kharade in this effort.
In general and product is positioned to provide a transactional MDM within Salesforce. We will cover the steps for implementation and some back ground on Fuzzy Matching or de-duplication.
We will walk thru the steps for setting up the tool.
- Cloud MDM Settings
- Cloud MDM Profile
- Adding Cloud related Information to Page Layout
- Synchronization Settings
- Data Cleansing
- Fuzzy Matching and Segments
- External Data Sources
- Consolidation and Enrichment
- Limitations
This post assumes familiarity with the Saleforce architecture.
1. Cloud MDM Settings
- Cloud MDM master on/off switch is configured using this setting and other settings like extracting the legal form and domain , overriding Salesforce Account information using Master bean after Match and Merge in Cloud MDM, and Standardizing Country.
- In some cases, you may wish to turn off Cloud MDM after you have installed and configured it.
- For example, if you wish to bring in a new set of data without creating beans. To achieve this, you need to switch Cloud MDM off.
2. Cloud MDM Profile:
- When Cloud MDM is installed, a default profile is given to all users. In order for your user to get access to all the features of Cloud MDM, you must configure an admin or super user profile. When you implement Cloud MDM, you can use profiles to assign MDM functionality to Salesforce user profiles.
- Users can have Permissions to Create/Update/Merge/consolidate Account, Contact and Leads, Create/Ignore duplicate Account, Contact and Leads, View consolidated information and create/Edit Hierarchy information
3. Add Cloud Related Information to Page Layout:
Helps to add MDM related components like Consolidated view, Find duplicates, MDM related fields like Synchronize, Legal forms, ISO country ,duplicate Account section, Related beans and Master Beans etc .
4. Synchronization Settings:
- This setting helps in Synchronizing/Mapping the Salesforce Attributes to Cloud MDM stage Area.
- We can map Standard fields and 10 custom fields. These standard and custom fields help us in configuring segment settings and match strategy in cloud MDM.
- Sync job helps creating beans and Master beans in cloud MDM stage Area.
5. Data Cleansing:
Data cleansing ensures the data is in a consistent format. Consistent data improves the quality of reporting and also improves matching results and the accuracy of duplicate detection.
Legal Form :
Legal form normalization is the process of extracting the legal form from the company norm and populating the legal form field with normalized data.
For example, We can configure the legal form field to contain normalized data for business entity designations such as Limited, Ltd., and L.T.D. We can add legal forms to the list available already after profoiling our data set.
Domain Normalization :
We can enable Cloud MDM to populate the domain field with a domain extracted from the website field. Cloud MDM uses the domain field during fuzzy matching.
For example, if a user enters http://www.acme.com/products or www. acme.com in the website field, Cloud MDM can populate the domain field with acme.com. normalized domain ensures domain field consistency and improves match results.
6. Fuzzy Matching and Segments:
Segment :
The segment field in the master bean record contains a matching segment. The matching segment is a string of characters that Cloud MDM uses to filter records before it performs fuzzy matching.
To improve fuzzy match performance, Cloud MDM performs an exact match on the matching segments to eliminate records that are unlikely to match. Cloud MDM then performs fuzzy matching on the remaining records. This can be basically creating Categories and Groups in Advanced Fuzzy Matching or “Blocking Indexes” Record Linkage. This will be created for all the Accounts once the Sync between Salesforce and MDM is done. It is also generated for external beans.
Fuzzy matching :
Fuzzy matching can match strings that are not exactly the same but have similar characteristics and similar patterns.
One example of a Fuzzy Matching algorithm is LevenShtein, the original Fuzzy algorithm Levenshtein Distance or Edit Distinceinvented in 1965
Levenshtein:
Counts the number of incorrect characters, insertions and deletions.
Returns:
(maxLen – mistakes) / maxLen
Levenshtein is a good algorithm for catching keyboarding errors
Matching is a two step process that determines a match score between two records. First, Cloud MDM performs an exact match on the matching segments to exclude records that are unlikely to have matches. Then, Cloud MDM performs a fuzzy match on the remaining records to calculate a match score between pairs of records. If the match score of the two records achieves the match score threshold, Cloud MDM considers the two records a match.
7. External Data Source:
We have external data in a system, such as SAP or Oracle EBS. We wish to load this data directly into beans, so we can take some of the information (SIC Code, No of Employees.) from the SAP record, and retain some information (e.g. Company Name) from the Salesforce record.
This setting allows us to configure the external Data source and defining the trust/priority score i.e. which value will win over the other during Consolidation and Enrichment process.
8. Consolidation and Enrichment.
Consolidation :
The consolidated view allows us to look at all beans associated with a master bean. In order to use this view, we must configure the fields that will display in the list of associated beans, as well as the account address information. This is done by configuring field sets.
Enrichment:
This setting allows us to over write the value from the Master bean to the Salesforce Org Account based on the trust/priority score provided during the configuration of the external Data source. We can use the override account option in cloud MDM settings to prevent the automatic override of the Salesforce Org Account accordingly.
9. Limitations.
There are two primary limitations:
- Custom Fields are limited to 10 and only 6 can be used in syncing.
- High volume matching from External Source is completed in a “Pre Match” process, which is basically accessing the “Master Bean” externally and developing ETL Process with another tool.
Metadata Mart the Road to Data Governance
Implementing a Metadata Mart the Road to Data Governance best viewed in PRESENTATION Mode, there is animation.
This presentation has narrative, play in presentation mode with sound on.
Self Service Semantic BI (Business Intelligence) Concept
 We want to build an Enterprise Analytical capability by integrating the concepts for building a Metadata Mart with the facilities for the Semantic Web
We want to build an Enterprise Analytical capability by integrating the concepts for building a Metadata Mart with the facilities for the Semantic Web
- Metadata Mart Source
- (Metadata Mart as is) Source Profiling(Column, Domain & Relationship)
- +
- (Metadata Mart Plus Vocabulary(Metadata Vocabulary)) Stored as Triples(subject-predicate-object) (SSIS Text Mining)
- +
- (Metadata Mart Plus)Create Metadata Vocabulary following RDFa applied to Metadata Mart Triple(SSIS Text Mining+ Fuzzy (SPARGL maybe))
- +
- Bridge to RDFa – JSON-LD via Schema.org
- Master data Vocabulary with lineage (Metadata Vocabulary + Master Vocabulary) mapped to MetaContent Statements)) based on person.schema.org
- Creates link to legacy data in data warehouse
- +RDFa applied to web pages
- +JSON-LD applied to
- + any Triples from any source
- Semantic Self Service BI
- Metadata Mart Source + Bridge to RDFa
I have spent some time in this for quite a while now and I believe there is a quite a bit of merit in approaching the collection of domain data and column profile data, in regards to the meta-data mart, and organize them in a triple’s fashion
The basis for JSON-LD and RDFa is the collection of data as a triple. Delving into said deeper
I believe with the proper mapping for the object reference and deriving of the appropriate predicates in the collection of the value we could gain some of the same benefits as well as bringing the web data being “collected, there by linking to source data.
Consider the following excerpt regarding Vocabularies derived from MetaContent via Metadata Structure
“Metadata structures[edit]
Metadata (metacontent), or more correctly, the vocabularies used to assemble metadata (metacontent) statements, are typically structured according to a standardized concept using a well-defined metadata scheme, including: metadata standards and metadata models. Tools such as controlled vocabularies, taxonomies, thesauri, data dictionaries, and metadata registries can be used to apply further standardization to the metadata. Structural metadata commonality is also of paramount importance in data model development and in database design.
Metadata syntax[edit]
Metadata (metacontent) syntax refers to the rules created to structure the fields or elements of metadata (metacontent).[11] A single metadata scheme may be expressed in a number of different markup or programming languages, each of which requires a different syntax. For example, Dublin Core may be expressed in plain text, HTML, XML, and RDF.[12]
A common example of (guide) metacontent is the bibliographic classification, the subject, the Dewey Decimal class number. There is always an implied statement in any “classification” of some object. To classify an object as, for example, Dewey class number 514 (Topology) (i.e. books having the number 514 on their spine) the implied statement is: “<book><subject heading><514>. This is a subject-predicate-object triple, or more importantly, a class-attribute-value triple. The first two elements of the triple (class, attribute) are pieces of some structural metadata having a defined semantic. The third element is a value, preferably from some controlled vocabulary, some reference (master) data. The combination of the metadata and master data elements results in a statement which is a metacontent statement i.e. “metacontent = metadata + master data”. All these elements can be thought of as “vocabulary”. Both metadata and master data are vocabularies which can be assembled into metacontent statements. “
The MetadataMart serve as the source for both metadata vocabulary and MDM for the Master Data Vocabulary.
For the Master Data Vocabulary consider schema.org which defines most of the schemas we need. Consider the following schema.org Persons Properties of Objects and Predicates:
A person (alive, dead, undead, or fictional).
| Property | Expected Type | Description |
| Properties from Person | ||
| additionalName | Text | An additional name for a Person, can be used for a middle name. |
| address | PostalAddress | Physical address of the item. |
The key is to link source data in the Enterprise via a Business Vocabulary from MDM to the Source Data Metadata Vocabulary from a Metadata Mart to conform the triples collected internally and externally.
In essence information from the web applications can be integrated with the dimensional metadata mart, MDM Model and existing Data Warehouses providing lineage for selected raw data from web to Enterprise conformed Dimensions that have gone thru Data Quality processes.
Please let me know your thoughts.
Guerrilla MDS MDM The Road To Data Governance
Watch “Guerrilla MDS MDM The Road To Data Governance” by @irawhiteside on @PASSBIVC channel here: youtu.be/U0TtQUhch-U #SQLServer #SQLPASS
For tomorrow’s MDM you must be ready to embrace Agile Iterative and/or Extreme Scoping in order to fully realize the benefits and learn the constraints of MDS















